How Manually Removing A Domain Controller Server
Thank to: https://argonsys.com/
Use of DCPROMO is still the proper way to remove a DC server in an Active Directory infrastructure. The following video provides an example of these steps:
Certain situations, such as server crash or failure of the DCPROMO option, require manual removal of the DC from the system by cleaning up the servers metadata. The following detailed steps will help you accomplish this:
Removing metadata via Active Directory Users and Computers
- Log in to DC server as Domain/Enterprise administrator and navigate to Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers
- Expand the Domain > Domain Controllers
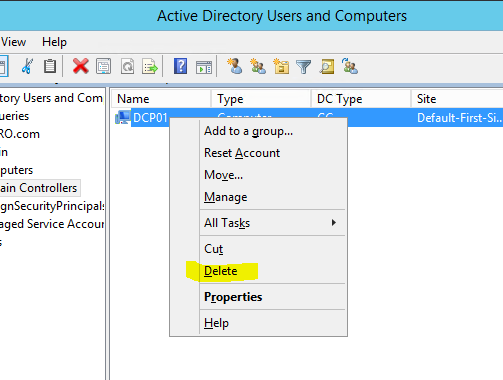
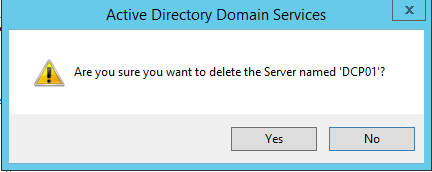
- Right click on the Domain Controller you need to manually remove and click Delete
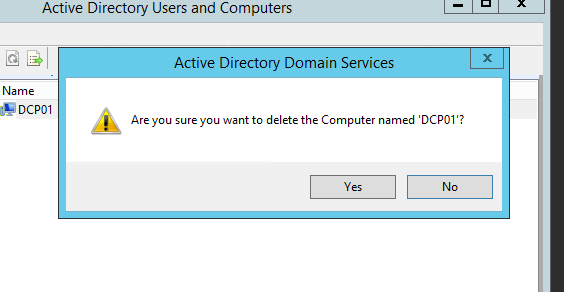
- Click Yes to confirm within the Active Directory Domain Services dialog box
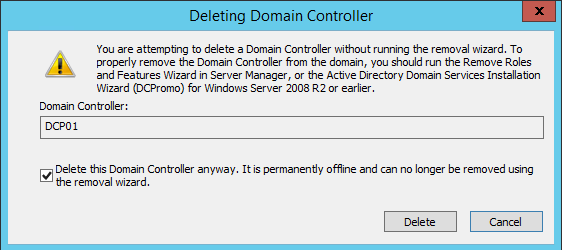
- In next dialog box, select This Domain Controller is permanently offline and can no longer be demoted using the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard (DCPROMO) and click Delete
- If the domain controller is global catalog server, in next window click Yes to continue with deletion
- If the domain controller holds any FSMO roles in next window, click Ok to move them to the domain controller which is available
Removing the DC server instance from the Active Directory Sites and Services
- Go to Server manager > Tools > Active Directory Sites and Services
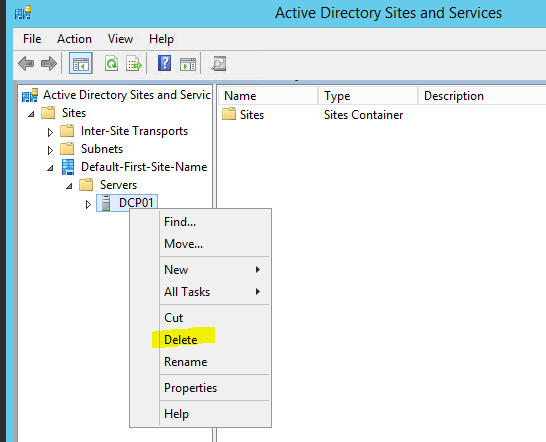
- Expand the Sites and go to the server which need to remove
- Right click on the server you which to remove and click Delete
- Click Yes to confirm
Remove metadata via ntdsutil
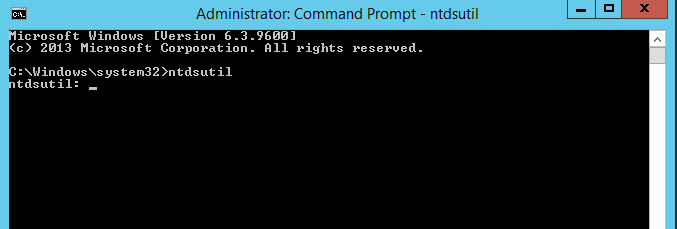
- Right Click on Start > Command Prompt (admin)
- Type ntdsutil and enter
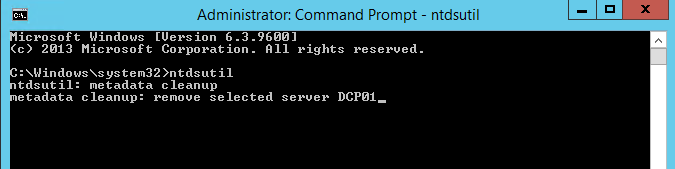
- You are then presented with the metadata cleanup prompt
- Next type remove selected server <servername>
NOTE: Replace <servername> with domain Controller server you wish to remove - Click Yes to proceed when presented with the warning window
- Execute the quit command twice to exit out of the console.
Incomplete addition or removal of a domain controller can lead to inconsistency in data due to the presence of a domain controller that exists, but is not completely functional. This hinders other processes and complete cleanup is required. The following steps describe how to cleanup the metadata.
- In the command line, type ntdsutil and press enter.
C:\WINDOWS→ntdsutil
You will see the following prompt displayed in the command prompt window:
ntdsutil: - At the Ntdsutil: prompt, type metadata cleanup
ntdsutil: metadata cleanup
Once you are done with that, the metadata cleanup prompt will appear like this:
metadata cleanup: - At the 'metadata cleanup:' prompt, type connections and press Enter.
metadata cleanup: connections
Now the server connections mode is on, as mentioned below:
server connections: - In 'server connections:', type :
connect to server < servername→Here <servername→ is the domain controller (any functional domain controller in the same domain) from which you plan to clean up the metadata of the failed domain controller. Press Enter after entering your server name. In this case, consider the server name to be server100. You will see the following entry.
server connections: connect to server server100
Binding to server100 ...
Connected to server100 using credentials of locally logged on user. - Type 'q' in server connections to quit and press Enter to return to the metadata cleanup prompt.
server connections: q
metadata cleanup: - In metadata cleanup, type select operation target and press Enter.
metadata cleanup: Select operation target
Now select operation target mode will come up.
select operation target: - Type list domains and press Enter.
select operation target: list domains
This lists all domains in the forest with a number associated with each.
Found 1 domain(s)
0 - DC=dorg,DC=net - Type select domain <number→, where <number→ corresponds to the domain in which the failed server was located. Press Enter.
select operation target: Select domain 0
We specify the number as 0 here, as the previous prompt let us know that 0 is the number assigned to the domain "dorg.net". Next you will see:
No current site
Domain - DC=dorg,DC=net
No current server
No current Naming Context - Type list sites and press Enter.
select operation target: List sites
The sites belonging to this domain are then listed as below:
Found 1 site(s)
0-CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,DC=net - Type select site <number→, where <number→ refers to the number of the site in which the domain controller was a member. Press Enter.
select operation target: Select site 0
We specify the number as 0 here, as the previous prompt let us know that 0 is the number assigned to the site available. Next you will see:
Site-CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,zC=net
Domain - DC=dorg,DC=net
No current server
No current Naming Context - Type list servers in site and press Enter.
select operation target: List servers in site
This will list all servers in that site with a corresponding number.
Found 2 server(s)
0-CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,DC=net
1-CN=SERVER100,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,DC=net - Type select server <number→ and press Enter, where <number→ refers to the domain controller to be removed.
select operation target: Select server 0
The number is 0 since we want to take out server200. You will be able to view:
Site-CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,DC=net Domain - DC=dorg,DC=net
Server-CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,DC=net
DSA-object-CN=NTDSSettings,CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers, CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg, DC=net DNS host name - server200.dorg.net
Computer object-CN=SERVER200,OU= Domain Controllers,DC=dorg,DC=net - Type 'q' to quit and press Enter. The Metadata cleanup menu is displayed.
select operation target: q
metadata cleanup: - Type "remove selected server" and press Enter. You will receive a warning message. Read it, and if you agree, press Yes.
metadata cleanup: Remove selected server
"CN=SERVER200,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,
CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=dorg,DC=net" removed from server "server100" - Type quit, and press Enter until you return to the command prompt to remove the failed server object from the sites.
- In Active Directory Users and Computers, expand the domain controllers container. Delete the computer object associated with the failed domain controller.
- Windows Server 2003 AD might display a new type of question window, asking you if you want to delete the server object without performing a DCPROMO operation . Select “This DC is permanently offline…” and click on the Delete button.
- AD will display another confirmation window. If you’re sure that you want to delete the failed object, click Yes to remove the failed server object from DNS.
- In the DNS snap-in, expand the zone that is related to the domain from where the server has been removed. Remove the CNAME record in the _msdcs.root domain of forest zone in DNS. You should also delete the HOSTNAME and other DNS records. If you have reverse lookup zones, also remove the server from these zones.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario
Dime si la información de este blog te sirvio.