How to monitor & automatically restart MySQL, Nginx, Apache etc. on your server
Thank to: https://superdevresources.com/
Managing server is not an easy job, specially if you have multiple softwares like MySQL, Nginx or Apache running on your servers. Downtime happens and running softwares get killed due to many reasons. In this post, I will share how I use Monit to constantly monitor programs running on my servers and automatically get them restarted when they go down. Monit also enables me to remotely watch the system status.
About Monit
Monit is a small Open Source utility for managing and monitoring Unix systems. Monit conducts automatic maintenance and repair and can execute actions in error situations.
Additionally, Monit has a built-in lightweight HTTP(S) interface you can use to browse the Monit server and check the status of all monitored services. From the web-interface you can start, stop and restart processes and disable or enable monitoring of services.
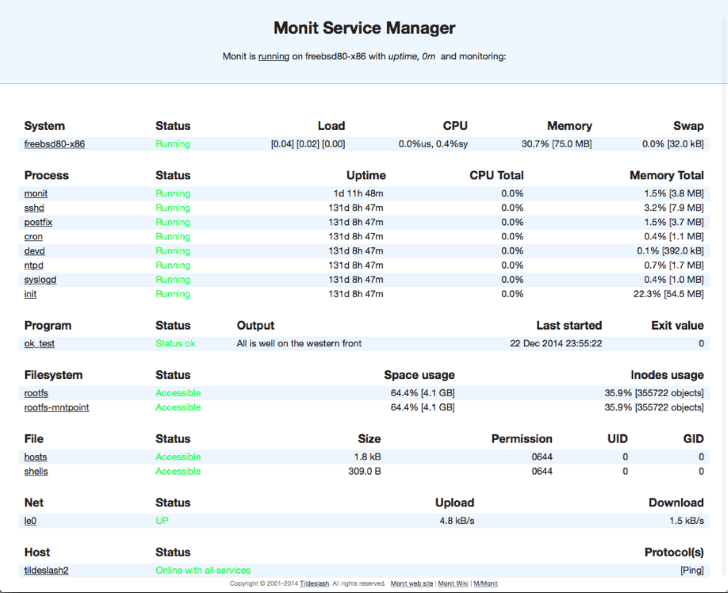
Installing and Configuring Monit on Ubuntu
We can install monit by simply running the following command
sudo apt-get install monitIt is very easy to configure Monit. I will show the very basic configurations required to enable the Monit Web interface and to monitor programs like MySQL, Nginx and Apache. Run the following command to open Monit configuration file in Vim editor:
sudo vim /etc/monit/monitrcEnabling Web Interface
The first thing we will do is enable the Web Interface for Monit, so that we can access it from anywhere. To configure the web interface, find and uncomment the section that begins with set httpd port 2812. If you wish, you can change the default port at which Monit web interface will be accessible. We are going to keep it same. Additionally, we will set a username and password for the web interface. You can also decide to give Read-Write or Read Only permissions based on user groups.
set httpd port 2812 and
# use address localhost # only accept connection from localhost
# allow localhost # allow localhost to connect to the server and
allow username:password # require user 'username' with password 'password'
# allow @monit # allow users of group 'monit' to connect (rw)
# allow @users readonly # allow users of group 'users' to connect readonlyMake sure to enable port 2812 on your server .
Monitoring and Automatically restarting MySQL with Monit
Add the following lines in Monit configuration file, for enabling monitoring of MySQL. Monit will restart MySQL whenever it is unable to find MySQL running.
check process mysqld with pidfile /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/mysql start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/mysql stop"Note that, you can add additional action and checks which I am not showing here. The above piece of configuration is sufficient to keep a watch on MySQL and restarting it in case of process termination.
Monitoring and Automatically restarting Nginx with Monit
Add the following lines in Monit configuration file, for enabling monitoring of Nginx. Monit will restart Nginx whenever it is unable to find a process for Nginx running.
check process nginx with pidfile /var/run/nginx.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/nginx start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/nginx stop"Monitoring and Automatically restarting Apache with Monit
Add the following lines in Monit configuration file, for enabling monitoring of Apache. Monit will restart Apache whenever it is unable to find Apache running.
check process apache with pidfile /run/apache2.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 stop"Note that, you can add additional check and actions for Apache too. Consult the Monit Documentation for full set of actions and checks possible.
Start Monit
Once you are done with editing the configuration file, all that is left is to start Monit/reload configuration and start monitoring of all services via the following commands.
sudo monit
sudo monit reload #in case monit was already started
sudo monit start allThat’s it. You should have Monit running and monitoring all the configured programs. You can check the status of Monit using the following command.
sudo monit statusOr simply connect to your server on port 2812 to access the Web Interface.
http://server_ip:2812Monit to the Rescue
I manage multiple servers, most of which are running WordPress which I have configured on Nginx and MySQL. Monit is a crucial tool for me to keep my websites and webapps running even when occasionally MySQL or some other service crashes. Of-course, this doesn’t mean that, you should not investigate the root cause of such crashes, but Monit will at-least help you keep your sanity while you are doing so. :)
Postgres & Monit
check process postgresql with pidfile /opt/postgres/data/postmaster.pid
group database
start program = "/etc/init.d/postgresql start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/postgresql stop"
if failed unixsocket /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 protocol pgsql then restart
if failed unixsocket /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 protocol pgsql then alert
if failed host localhost port 5432 protocol pgsql then restart
if failed host localhost port 5432 protocol pgsql then alert
if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
check process postgresql with pidfile /opt/postgre//data/postmaster.pid
group database
start program = "/opt/postgres/bin/pg_ctl start"
as uid postgres and gid postgres
stop program = "/opt/postgres/bin/pg_ctl stop"
as uid postgres and gid postgres
if failed unixsocket /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 protocol pgsql then restart
if failed unixsocket /tmp/.s.PGSQL.5432 protocol pgsql then alert
if failed host localhost port 5432 protocol pgsql then restart
if failed host localhost port 5432 protocol pgsql then alert
if 5 restarts within 5 cycles then timeout
Monitoring Messages Generated
ESTrootFATAL: database "root" does not exist
1. Create DB user `root'.
2. Create a database 'root' owned by root. It doesn't need to contain any data.
3. Add these descriptions to pg_hba.conf;
host root root 127.0.0.1/32 trust <= for test via TCP port
local root root ident sameuser <= for test via UNIX socket
if failed host localhost port 5432 type TCP then restart if failed host localhost port 5432 type TCP then alert


Comentarios
Publicar un comentario
Dime si la información de este blog te sirvio.