Metadata Cleanup Using NTDSUTIL in Windows Server 2008 R2
Thank to: http://www.msserverpro.com
1. Open a command prompt, type ntdsutil and press Enter.
2. At the Ntdsutil prompt, type metadata cleanup and press Enter.
3. At the Metadata Cleanup prompt type connections and press Enter.
4. At the Server Connections prompt, type connect to server KTM-DC02-2K8
(where KTM-DC02-2K8 is the name of an available domain controller which holds Operations Masters Roles)
(If you have not logged on using an account that is a member of the Enterprise Admins group, you can set your credentials at this point by typing set creds domainname username password and then press Enter)
5. At the Server Connections prompt, type quit and press Enter.
6. At the Metadata Cleanup prompt, type select operation target and press Enter.
7. At the Selected Operations Target prompt, type list domains and press Enter. This list all the domains in the forest are listed with a number associated to each.
8. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type select domain 0, where number “0” is the failed domain controller, and press Enter.
9. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type list sites and press Enter. This list all the sites in the forest are listed with a number assigned to each.
10. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type select site 0, where number “0” is the site containing the failed domain controller, and press Enter.
11. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type list servers in site and press Enter.
12. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type select server 0, where number “0” is the failed domain controller, and press Enter.

13. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type quit and press Enter.
14. At the Metadata Cleanup prompt, type remove selected server and press Enter.

15. You will receive a warning message. Read it, and if you agree, Click Yes to confirm removal of the server.


16. Type quit at each prompt to exit Ntdsutil.

In addition to cleaning up the Active Directory object using Ntdsutil, we should clean up the DNS records for the failed domain controller. Remove all DNS records from DNS, including all domain controller records, GC server records, and PDC emulator records. (The last two will exit only if the domain controller was configured with these roles.) If you do not clean up the DNS records, clients will continue to receive the DNS information and try to connect to the domain controller. This can result in slower connections to Active Directory as clients fail over to use alternate domain controllers.
1. Open DNS Manager, expand Forward Lookup Zones, Right Click _msdcs.msserverpro.com, Click Properties.

2. On the _msdcs.msserverpro.com Properties dialog box, Click on Name Server Tab, select the offline domain controller and Click on Remove
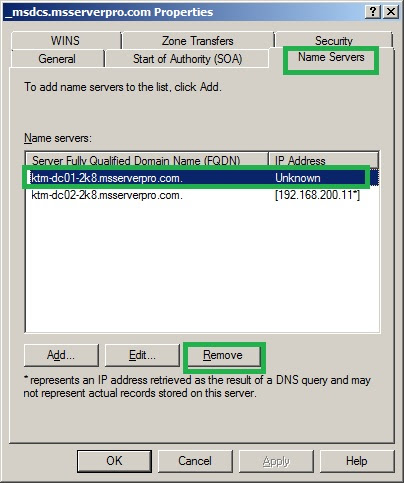
3. Click Apply and Click OK.

4. Right Click on mssserverpro.com, and then click Properties.

5. On the msserverpro.com Properties dialog box, Click on Name Servers Tab, select the offline domain controller and Click on Remove.

6. Click Apply and then Click OK.

7. Do the same process on Reverse Lookup Zones.

8. Remove all DNS records (KTM-DC01-2K8.msserverpro.com) from DNS, including all domain controller records, GC server records and PDC records.



9. Open Active Directory Sites and Services; expand Default-First-Site-Name, Servers, Right Click on KTM-DC01-2K8, Click Delete.

10. On Active Directory Domain Services dialog box, Click Yes.

11. Close the Active Directory Sites and Services Console.
This process of removing data in
AD DS is known as Metadata Cleanup. NTDSUTIL is used to clean up domain
controller metadata. If a domain controller that is damaged and cannot
be started from Active Directory service, we can then use NTDSUTIL to
clean out the unsuccessful domain controller demotion, and it is very
important that you do so. This will solve problems with slow login in
domain controller, replication as well as knowledge Consistency Checker
(KCC).
Here, KTM-DC01-2K8.msserverpro.com server is a failed domain controller, which we want to remove. To do this, we will use the NTDSUTIL command line tool.
Follow these steps to clean up the directory from a failed domain controller:1. Open a command prompt, type ntdsutil and press Enter.
2. At the Ntdsutil prompt, type metadata cleanup and press Enter.
3. At the Metadata Cleanup prompt type connections and press Enter.
4. At the Server Connections prompt, type connect to server KTM-DC02-2K8
(where KTM-DC02-2K8 is the name of an available domain controller which holds Operations Masters Roles)
(If you have not logged on using an account that is a member of the Enterprise Admins group, you can set your credentials at this point by typing set creds domainname username password and then press Enter)
5. At the Server Connections prompt, type quit and press Enter.
6. At the Metadata Cleanup prompt, type select operation target and press Enter.
7. At the Selected Operations Target prompt, type list domains and press Enter. This list all the domains in the forest are listed with a number associated to each.
8. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type select domain 0, where number “0” is the failed domain controller, and press Enter.
9. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type list sites and press Enter. This list all the sites in the forest are listed with a number assigned to each.
10. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type select site 0, where number “0” is the site containing the failed domain controller, and press Enter.
11. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type list servers in site and press Enter.
12. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type select server 0, where number “0” is the failed domain controller, and press Enter.
13. At the Select Operations Target prompt, type quit and press Enter.
14. At the Metadata Cleanup prompt, type remove selected server and press Enter.
15. You will receive a warning message. Read it, and if you agree, Click Yes to confirm removal of the server.
16. Type quit at each prompt to exit Ntdsutil.
In addition to cleaning up the Active Directory object using Ntdsutil, we should clean up the DNS records for the failed domain controller. Remove all DNS records from DNS, including all domain controller records, GC server records, and PDC emulator records. (The last two will exit only if the domain controller was configured with these roles.) If you do not clean up the DNS records, clients will continue to receive the DNS information and try to connect to the domain controller. This can result in slower connections to Active Directory as clients fail over to use alternate domain controllers.
1. Open DNS Manager, expand Forward Lookup Zones, Right Click _msdcs.msserverpro.com, Click Properties.
2. On the _msdcs.msserverpro.com Properties dialog box, Click on Name Server Tab, select the offline domain controller and Click on Remove
3. Click Apply and Click OK.
4. Right Click on mssserverpro.com, and then click Properties.
5. On the msserverpro.com Properties dialog box, Click on Name Servers Tab, select the offline domain controller and Click on Remove.
6. Click Apply and then Click OK.
7. Do the same process on Reverse Lookup Zones.
8. Remove all DNS records (KTM-DC01-2K8.msserverpro.com) from DNS, including all domain controller records, GC server records and PDC records.
9. Open Active Directory Sites and Services; expand Default-First-Site-Name, Servers, Right Click on KTM-DC01-2K8, Click Delete.
10. On Active Directory Domain Services dialog box, Click Yes.
11. Close the Active Directory Sites and Services Console.

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario
Dime si la información de este blog te sirvio.